This is a tutorial on how to start developing Web APIs with EF Migrations on Ubuntu/Linux Mint using SQL Server. This project also works on Windows, just need to update the connection string.
First install .Net Core: https://www.microsoft.com/net/core#linuxubuntu
Then install Visual Studio Code:
https://code.visualstudio.com/Download
If your VS Code main window is blank, edit start command and add code --disable-gpu
Then install SQL Server: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-setup-ubuntu And SQL Server command-line tools: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-setup-tools#ubuntu Now you can test the instalation: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-connect-and-query-sqlcmd
Now let's create the project, there are two options, via dotnet new and yeoman.
dotnet new webapi
You should get this: The template "ASP.NET Core Web API" created successfully.
Then restore packages, build and run:
dotnet restore
dotnet build
dotnet run
A server will start on localhost:5000. You can test sample controller by navigating to http://localhost:5000/api/values ,will get ["value1","value2"].
At this point you can open the folder with Visual Studio Code. If it suggests to install some extensions, just do it.
Add a folder Contextand a file inside it Context.cs. inside it add:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace testApi.Context
{
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{ }
public DbSet<Item> Items { get; set; }
}
public class Item
{
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
Always change the namespace to match your app's namespace.
Now add a connection string in appsettings.json and/or appsettings.Development.json:
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection":"Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=AppDbContext;User ID=sa;Password=TypeYourPassHere"
},
Now edit ConfigureServices in Startup.cs:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// Add framework services.
services.AddMvc();
services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
}
You also need to add some packages, so edit CoreMigrationsWebApi.csproj or what name you gave it:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp1.1</TargetFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<Folder Include="wwwroot\" />
</ItemGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore" Version="1.1.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc" Version="1.1.2" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Debug" Version="1.1.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer" Version="1.1.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.Design" Version="1.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools" Version="1.0.0"/>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design" Version="1.0.3" />
</ItemGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<DotNetCliToolReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools.DotNet" Version="1.0.0"/>
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
At this point you can create the database by running:
dotnet ef migrations add InitialMigration
dotnet ef database update
P.S. always run these commands after making a change in code or adding a package:
dotnet restore
dotnet build
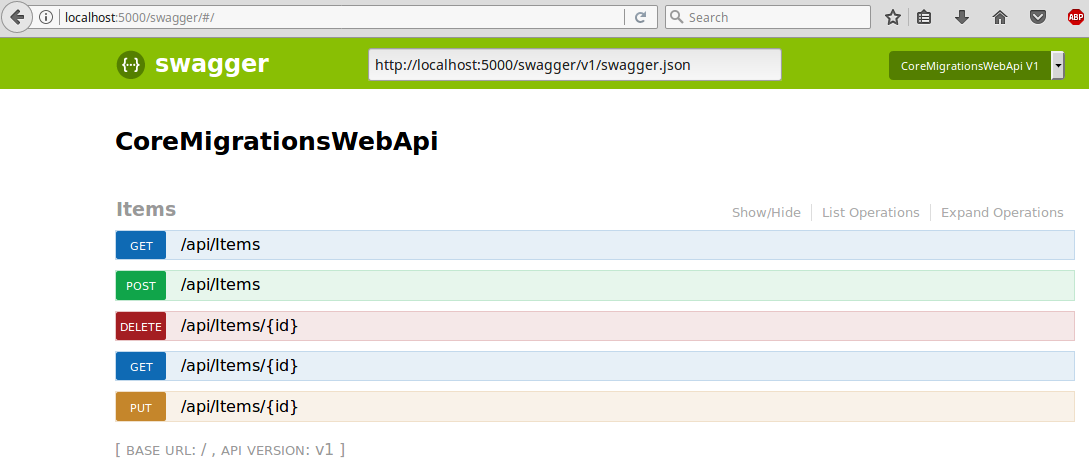
Now that we have the database set up, we can add a controller with basic CRUD operations:
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using testApi.Context;
using testApi.ViewModels;
namespace CoreMigrationsWebApi.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class ItemsController : Controller
{
private readonly AppDbContext _context;
public ItemsController(AppDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// GET api/items
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get()
{
var dbItems = _context.Items.ToList();
var viewModel = new ItemsViewModel
{
Items = dbItems.Select(x => new ItemViewModel
{
Id = x.Id,
Name = x.Name,
}).ToList(),
Count = dbItems.Count,
};
return Ok(viewModel);
}
// GET api/items/5
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public IActionResult Get(int id)
{
var dbItem = _context.Items.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == id);
if (dbItem == null)
{
return NotFound("item not found!");
}
return Ok(new ItemViewModel { Id = dbItem.Id, Name = dbItem.Name });
}
// POST api/items
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Post([FromBody]ItemViewModel item)
{
var newDbItem = new Item { Name = item.Name };
try
{
_context.Items.Add(newDbItem);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
catch
{
return BadRequest();
}
return Get(newDbItem.Id);
}
// PUT api/items/5
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public IActionResult Put(int id, [FromBody]ItemViewModel item)
{
var dbItem = _context.Items.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == id);
if (dbItem == null)
{
return NotFound("item not found!");
}
try
{
dbItem.Name=item.Name;
_context.SaveChanges();
}
catch
{
return BadRequest();
}
return Get(id);
}
// DELETE api/items/5
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int id)
{
var dbItem = _context.Items.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == id);
if (dbItem == null)
{
return NotFound("item not found!");
}
try
{
_context.Items.Remove(dbItem);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
catch
{
return BadRequest();
}
return Ok("Delete successful");
}
}
}
You will also need the view models located in ViewModels folder.
namespace testApi.ViewModels
{
public class ItemViewModel
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace testApi.ViewModels
{
public class ItemsViewModel
{
public List<ItemViewModel> Items { get; set; }
public int Count { get; set; }
}
}
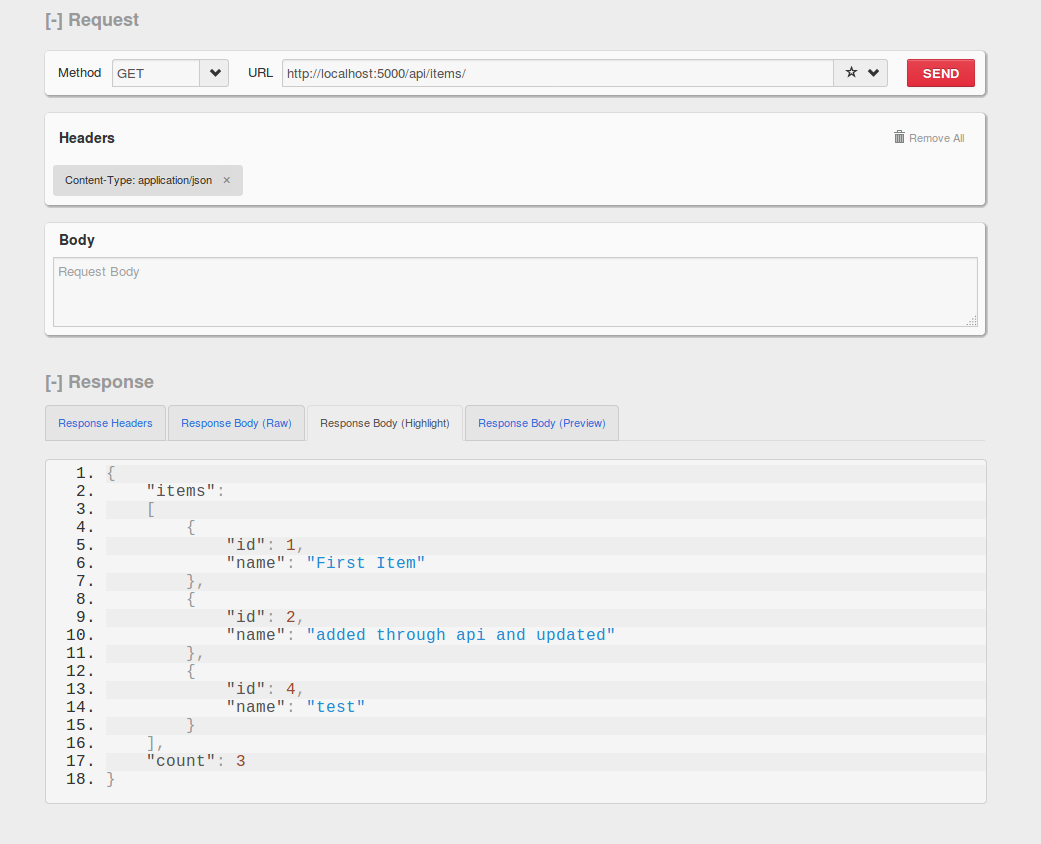
Now run the project and test the endpoints with Postman or RESTClient or any other you prefer. Don't forget about Content-type: application/json; header.
Here is an example for get/items: