- Team Lead: Yimin Zheng @Mr-Milk
- Team Members: Arkajyoti Sarkar @arka2696, Sunag Parasu @sunagparasu
Stain normalization is a critical preprocessing step in computational pathology that addresses color variations caused by differences in staining protocols, scanners, and tissue preparation techniques. These variations can significantly impact the performance of downstream analysis tasks.
Recent research has shown that many histology foundation models fail to adequately eliminate staining batch effects (see this paper), which negatively impacts multimodal integration and biomarker prediction accuracy.
This project delivers GPU-accelerated stain normalization algorithms using CuPy, providing substantial performance improvements on CUDA-enabled GPUs for large-scale histology image processing workflows.
During the hackathon, we successfully implemented and benchmarked three widely-used stain normalization methods:
- Reinhard normalization
- Histogram matching
- Macenko normalization
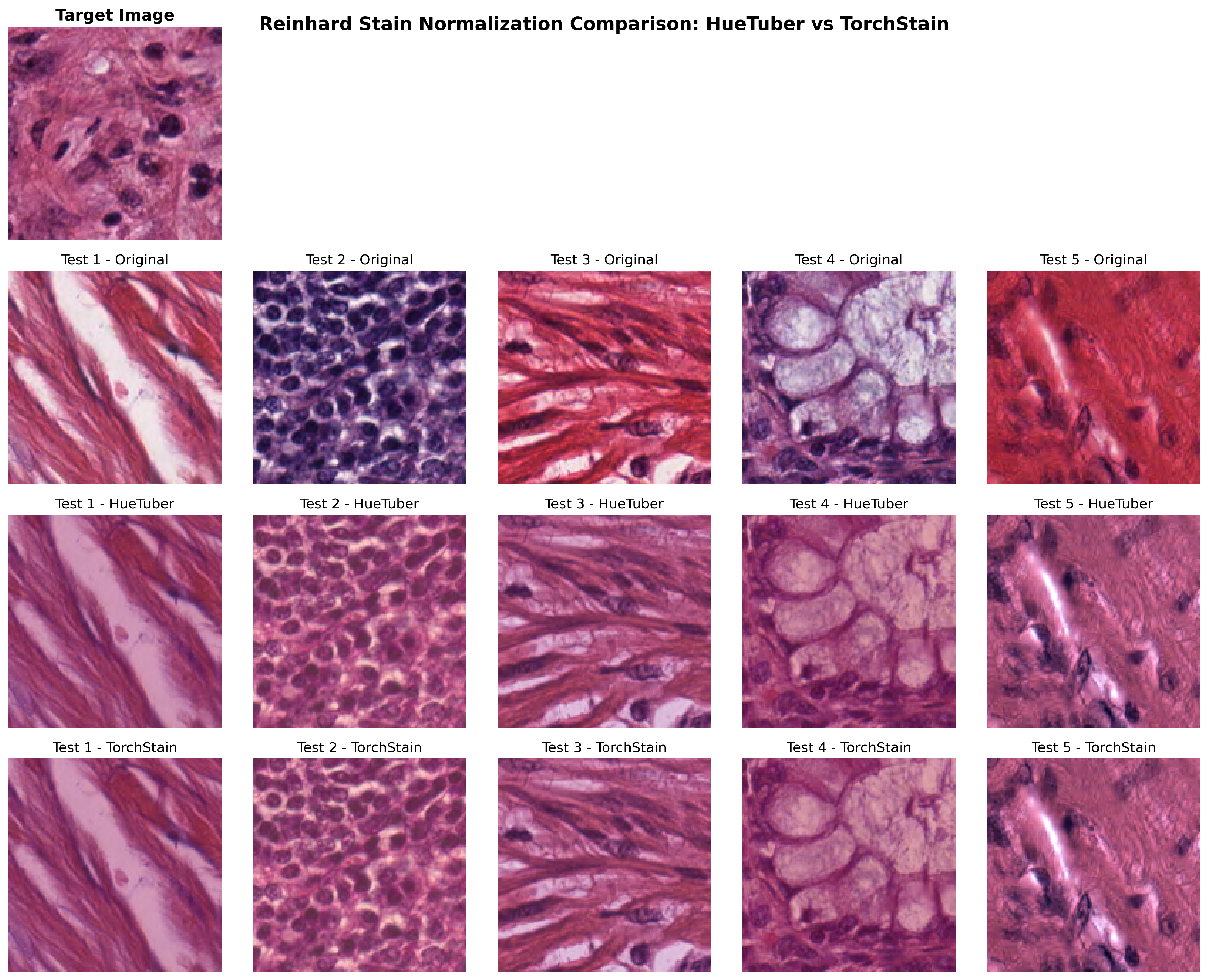
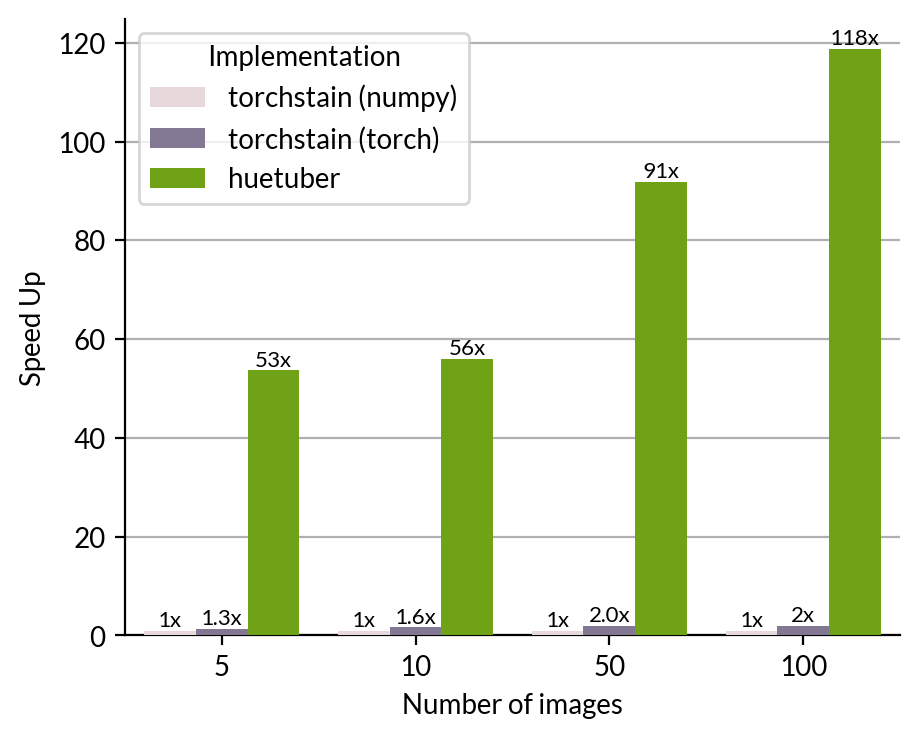
Our GPU-accelerated Reinhard implementation achieves 50-100x speedup compared to the NumPy-based torchstain implementation while maintaining identical visual results.
Visual Validation
Performance Benchmark
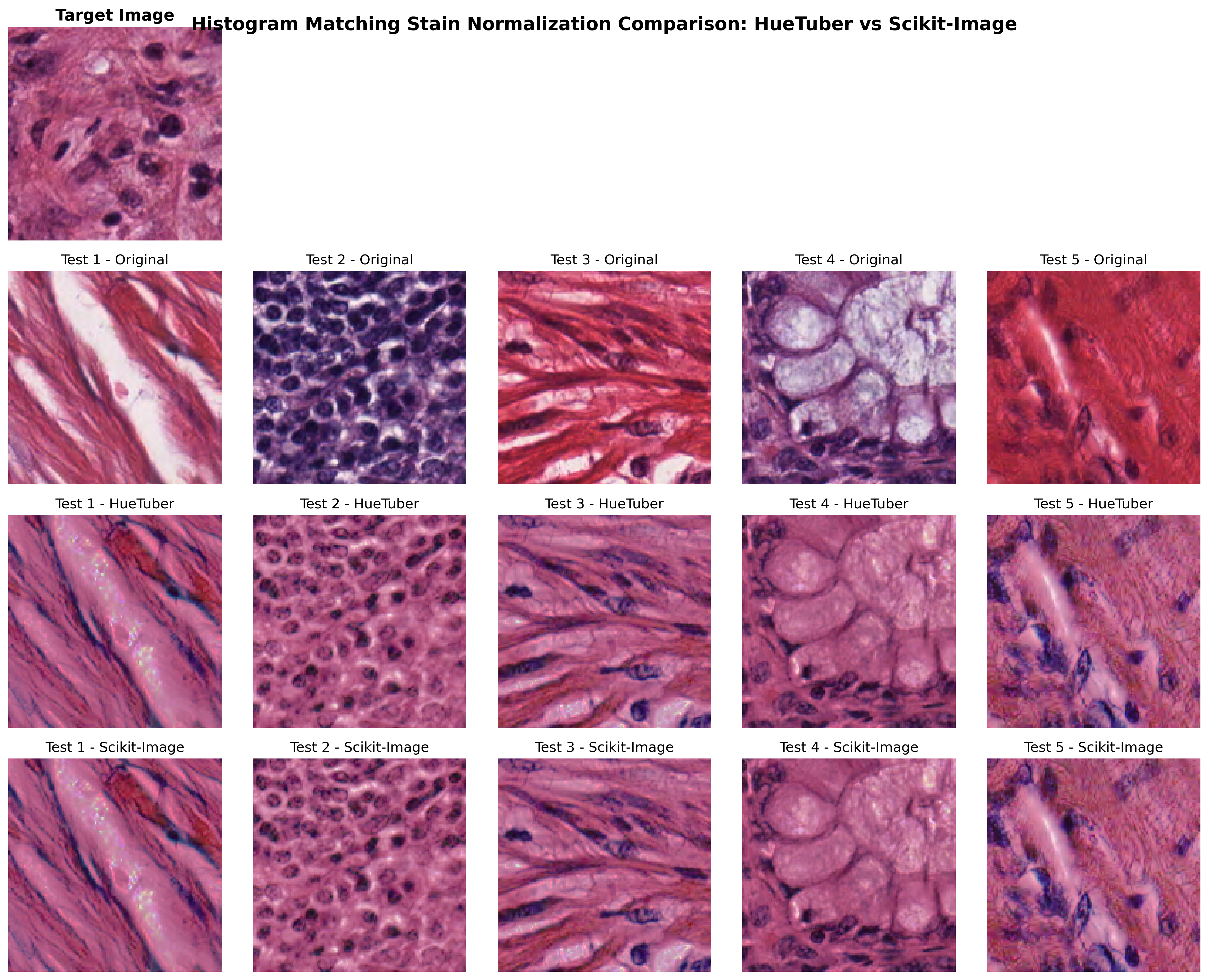
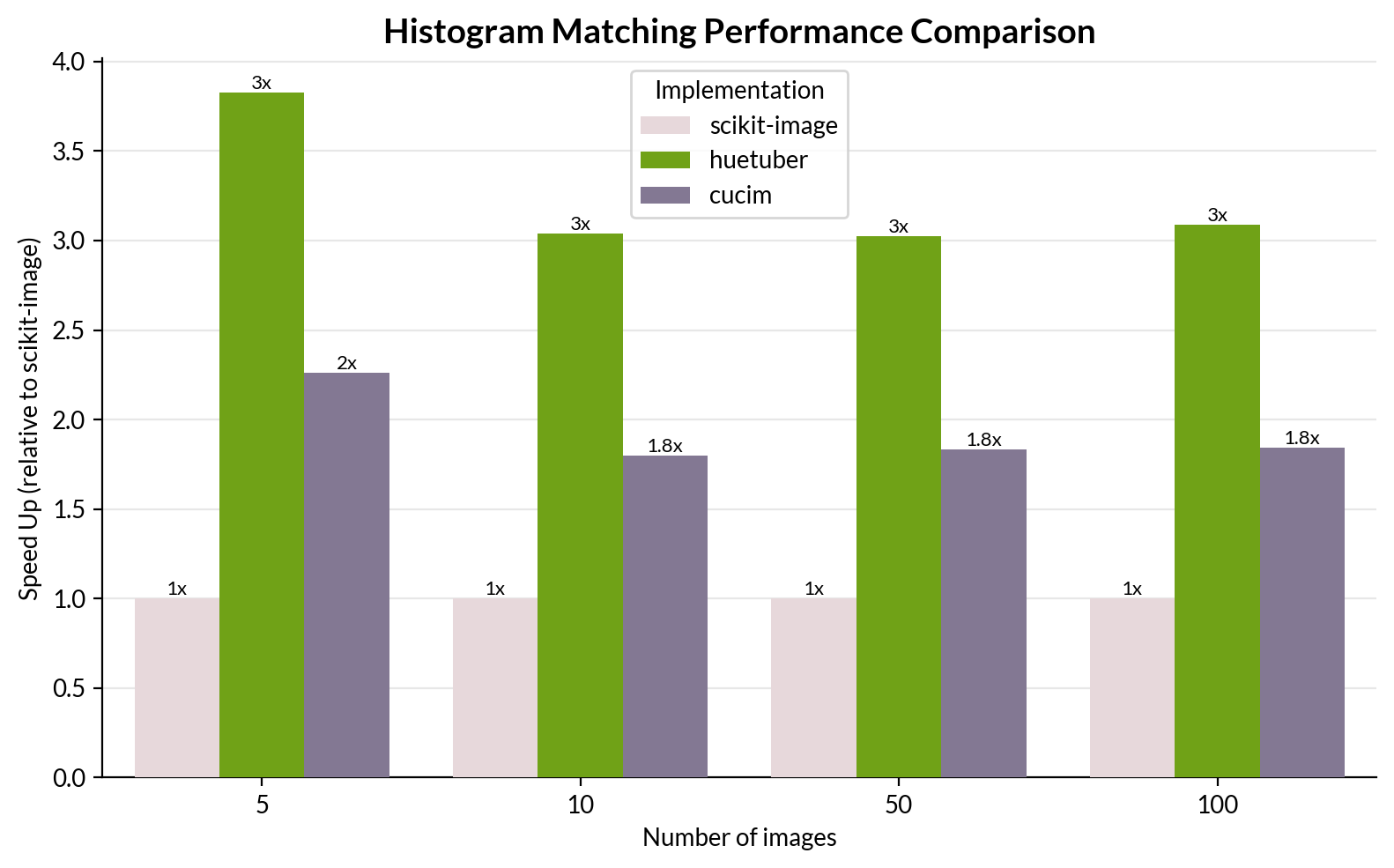
Our histogram matching implementation not only matches scikit-image results but also outperforms existing GPU implementations, including RAPIDS cuCIM.
Visual Validation
Performance Benchmark
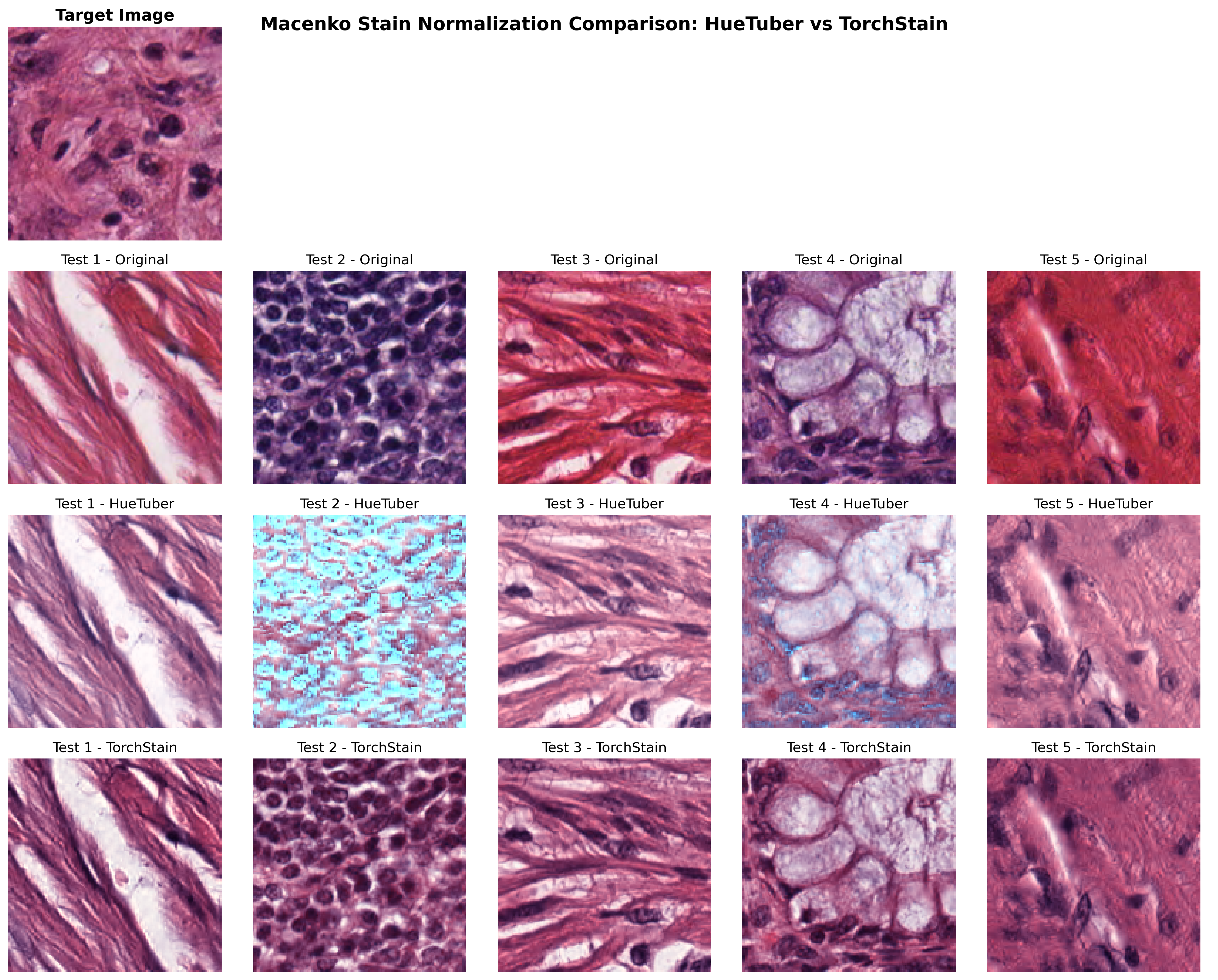
While our Macenko implementation demonstrates the feasibility of GPU-accelerated stain separation, the results do not yet fully replicate existing implementations. This remains an area for future development.
Visual Comparison
-
High-performance computing: Achieved 50-100x speedup for Reinhard normalization compared to existing CPU implementations
-
Algorithm fidelity: Successfully replicated visual results of established implementations for Reinhard and histogram matching methods
-
Competitive performance: Outperformed existing GPU implementations, including RAPIDS cuCIM, for histogram matching
- Optimize Macenko stain separation algorithm to match reference implementation accuracy
- Extend support for additional stain normalization methods (e.g., Vahadane)
- Integrate with popular computational pathology frameworks